|
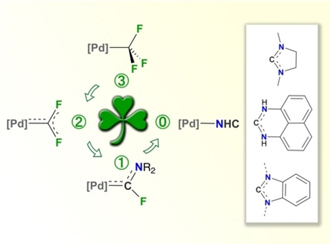
The homoleptic trifluoromethyl-palladium(II) complex [Pd(CF3)4]2- (1) is shown to be highly active towards amines. Thus, when treated with primary amines RNH2, it readily undergoes aminolysis of one of the CF3 ligands affording the isocyanide complexes [(CF3)3Pd(CNR)]- (R=aryl). In this process the original CF3 group undergoes total defluorination. Interestingly, the reaction of 1 with secondary amines R2NH proceeds with loss of just two F-substituents, whereby the Fischer-type fluoroaminocarbene complexes [(CF3)3Pd(CFNR2)]- are formed (R=Et, Ph). The reaction of 1 with diamines affords different [(CF3)3Pd(NHC)]- complexes containing sterically non-demanding NHC ligands. Representative examples of various topologies are reported based on the common imidazolidin-2-ylidene or benzimidazolin-2-ylidene rings as well as the expanded-ring perimidin-2-ylidene. This metal-tailored synthetic route, where a CF3 group acts as a pre-carbenic unit, is unprecedented in the vast NHC-chemistry. It takes place under very mild conditions and is envisaged to be extensible to other non-isolable NHC ligands. The key difluorocarbene intermediate [(CF3)3Pd(CF2)]- is experimentally detected.
|